Last Updated on February 19, 2017 by Dr.Derek Fhisher
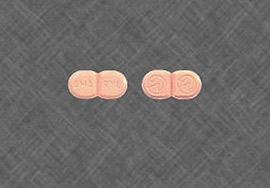
Most popular brand: Amaryl
Active ingredient: Glimepiride
Available dosage forms: 1, 2, 4 mg

Buy Glimepiride without a prescription or Generic Amaryl from 500mg.org and get excellent drug on reduced global costs. To purchase Glimepiride online will be to have much more privacy than what’s accessible when taking a prescription to a pharmacy that is local. 500mg.org offers you the chance to buy affordable Glimepiride 1, 2, 4 mg online and also find out more about Glimepiride side effects, dosage information and drug interactions. Ask your pharmacist any questions you might have relating to Glimepiride, especially if it’s new to you. Buy generic Amaryl online at the finest affordable price from 500mg.org and get your Glimepiride pills sent at your doorstep in time. The foremost benefit of purchasing prescription medicines like Amaryl and other medical supplies from 500mg.org is the secure buying process as well as the dedication to providing finest care and keeping the common up to the mark. Being able have other prescriptions or to buy Glimepiride online saves effort, time, and the price of a lengthy excursion. They have the power to compare prices more easily when people purchase Glimepiride online. By contrast, the best on-line sources for prescription drugs like Glimepiride frequently have extensive drug information right on the website, so consumers can get replies to their questions quickly and readily when they buy Glimepiride 1, 2, 4 mg online, and they could easily print out the tips for future reference. However, accessibility to an authorized pharmacist is a phone call away when folks purchase Glimepiride online with trustworthy online sources.
Glimepiride general information
Commonly suggested for individuals with panic disorder issues, weight change isn’t a bothersome side effect. It may likewise induce difficulty in breathing, or possibly a feeling of breathlessness. The individual might feel tired constantly, and even drowsy sometimes. Therefore, attempt to be in a positive mindset and steer clear of thoughts which are a generator of strain and anxiety.
There aren’t any particular skin or blood tests accessible to diagnose sulfa allergy. Certain drugs are reported to interact with colchicine and raise the severity of its own side results. Sulfa drugs are by and large know to result in allergies, thus, the medications ought to be carefully prescribed. Ergo, if you intend to get yourself some type of treatment with it, you need to consult with a herbalist.
Carnitine can play a significant role in lessening the degree of cholesterol, particularly the harmful LDL cholesterol in the entire body. In such instances, people take magnesium oxide supplements, to be able to maintain its regular levels in the entire body. Digestive disorders, like, indigestion, and heartburn, will likely stay under control once the consistency of magnesium oxide is maintained. SSRIs boost mood by upping serotonin level within the brain.
An allergy to sulfa drugs too can worsen asthma owing to its influence on the lungs. For example, a patient of kidney disease, should consult the physician about the fluid and also water intake. The side effects can be mild or severe, conditioned upon the age and total well-being of the patient. In case the allergy symptoms are extremely severe, the individual ought to be treated by means of an allergist, who’s experienced within the management of drug allergies.
Gout attacks are recurrent and painful and hence, someone must certanly be careful when planning the dietary plan. Iron deficiency could be observed in a number of men and women, caused if their diet lacks the vital nutrients, especially iron. The diet to stop gout must contain very low protein and very low calorie foods.
Here’s a list of its own side outcomes. This list is perpetually being updated and revised, so should you find adverse interactions, your own doctor may simply have the capacity to switch you to another drug that’ll treat something similar. In conclusion, we can say, should you be taking flomax, and notice some of the aforementioned unwanted side effects, don’t delay in contacting your doctor to elucidate the circumstance, and stop the long-term ill outcomes. Dangerous and risky unwanted side effects of the drug are seizures and irregularity within the heartbeat. You ought to follow the directions of your own physicians religiously while taking this medication.
Ferrous sulfate supplies the body with sufficient iron to help treat or prevent diseases and healthcare circumstances, which are caused because of deficiency of iron in the entire body, like anemia. Within this disease, uric acid crystals become deposited on the joints, leading to joint pain as well as inflammation. Therefore, it is used within the treatment of a broad selection of ailments. At the similar time, an iron deficiency may also be caused because of excessive bleeding another health issue. This in the majority of cases is on account of the presence of iron within them.
Ferrous sulfate can result in an allergic reaction in certain people, leading to a skin rash or itching. Additionally It is useful in another viral disease, referred to as shingles, which is distinguished by skin rashes. It may likewise have an impact on the epidermis, which makes it paler than usual. In several cases, an elevated sensitivity to sunlight (photosensitivity) might also be observed.
Gout is a form of arthritis, which is related to excruciating pain within the joints. L-lysine can help alleviate the symptoms connected with the heart condition, generally known as angina pectoris, when taken together with vitamin C. Both the nutrients are found to work in cutting chest pain, related to this condition. The main utilization of colchicine is it can relieve pain as well as inflammation brought on by gout disease, which is distinguished by defective uric acid metabolism. Lysine supplements may also be required in some specific medical conditions that bring about protein loss, for example large wounds and burns. Consequently, It’s critical to maintain a normal check on its levels through blood and urine tests so as to stop the occurrence of any sort of kidney diseases. Normal exercise aids in controlling high blood glucose level and in addition prevents the side effects of the drug.
So far As the dosage is concerned, it is usually better to speak to your health care provider. As a way to avert these problems, it’s quite essential to seek advice from a doctor before beginning the intake of the medicine. Moreover, be certain to consult a seasoned physician prior to taking lysine supplements, particularly if you have a health problem or you’re taking any sort of medication. It’s likewise more advisable to prevent this medicine when pregnant and breastfeeding. Together with proper diet and medications, in the event the patient is overweight, he then needs to keep up the weight with the right workouts to eliminate excess weight.
Active – active substance / start: glimepiride
Amaryl; Glemaz; Gliamal (Gliamal Pliva); glimepiride; Glyumedeks; Meglimid.
glimepiride – oral hypoglycemic agent; derivative III generation sulfonylureas. It stimulates the secretion of insulin beta – cells of the pancreas, increases the release of insulin and insulin – sensitive receptors in the cells – the target, increases the sensitivity of peripheral tissues to insulin inhibits gluconeogenesis. It is used to treat non-insulin dependent diabetes mellitus (type 2 diabetes) in the case of poor diet, physical exercise and weight loss. Reduces the risk of retinopathy, neuropathy and nephropathy.
Active – active substance:
glimepiride / Glimepiride.
Dosage Forms:
Tablets.
glimepiride
Properties / Action:
Glimepiride is an oral hypoglycemic agent initially prolonged action; derivative III generation sulfonylureas.
Glimepiride stimulates the secretion of insulin beta – cells of the pancreas and increases insulin release. It increases the number of insulin – sensitive receptors in the cells – the target, increases the sensitivity of peripheral tissues to insulin inhibits gluconeogenesis. It improves postprandial insulin / C – peptide response, reduces hyperglycemia without increasing the level of insulin / C – peptide on an empty stomach.
Glimepiride reduces the risk of retino -, neuro – and nephropathy.
When combined appointment of glimepiride can reduce the dose of insulin in obese patients by 38%.
The maximum effect of glimepiride achieved after 2 – 3 hours, hypoglycemic effect lasts longer than 24 hours.
Pharmacokinetics:
Glimepiride has a high absorption and absolute bioavailability (100%). Food intake has no significant effect on absorption. Maximum serum concentrations of glimepiride (Cmax) are reached approximately 2.5 hours. It has a very low distribution volume (approximately 8.8 liters) approximately equal to the volume of distribution of albumin, and low ground clearance (about 48 ml / min). Relations with proteins – 99%. It is metabolized in the liver to hydroxylated and carboxylated derivatives. The half-life of 5 – 8 hours. After receiving high-dose half-life of glimepiride is increased. Write mainly in the form of metabolites; 58% found in the urine and 35% – in the feces. Glimepiride Unchanged in the urine was not found. By comparing the data obtained with single dose and multiple dose glimepiride for several days once a day 1, revealed no significant differences in pharmacokinetics. No significant accumulation of glimepiride were observed.
The pharmacokinetic parameters are similar to glimepiride in patients of different sexes and different age groups. In patients with impaired renal function (low creatinine clearance) tended to increase clearance of glimepiride and a decrease in its average serum concentrations. In these patients there is no additional risk of cumulation Glimepiride.
Indications:
By reducing the effectiveness of glimepiride (partial secondary resistance) can be administered in combination with oral hypoglycemic drugs containing metformin. or insulin preparations (short-acting insulin. intermediate-acting insulin. long-acting insulin. Insulin biphasic).
Dosage and administration:
The initial and maintenance dose of glimepiride are determined on the basis of regular monitoring of glucose levels in blood and urine. A monitor for monitoring blood sugar levels in the urine and also helps to detect primary or secondary resistance to glimepiride.
Glimepiride Tablets taken orally as a whole, without chewing, with a sufficient amount of liquid (about 0.5 cups).
The starting dose and titration of glimepiride:
Usually, at the beginning of treatment prescribed 1 mg glimepiride once daily. the daily dose can be increased if necessary. Any increase in the dose of glimepiride should be conducted at regular control of blood sugar levels gradually (e.g., at intervals of 1 – 2 weeks) and as follows: 1 mg – 2 mg – 3 mg – 4 mg – 6 mg, and (exceptionally ) – 8 mg.
The range of daily doses of glimepiride in patients with well-controlled diabetes:
A typical daily dose range of glimepiride in patients with well-controlled diabetes is 1 to 4 mg. Only individual patients sufficient effect is achieved by the daily doses of more than 6 mg.
The distribution of the daily dose of glimepiride:
Time and allocation of receiving a daily dose of glimepiride is determined by a physician taking into account the way of life of the patient. Usually it is enough to take the daily dose once a day. This should be done immediately before a hearty breakfast, or if the daily dose has not been accepted, immediately before the first abundant meal. It is very important not to skip meals after taking glimepiride.
The secondary correction dose of glimepiride:
In the case of improvement of diabetes compensation increases insulin sensitivity in this regard, in the course of treatment may decrease the need for glimepiride. In order to avoid the development of hypoglycemia should be considered for temporary dose reduction or cancellation of glimepiride.
dose adjustment should be carried out as in patient weight change or change his way of life, or the appearance of other factors that contribute to increased susceptibility to the development of hypo – or hyperglycaemia.
The duration of treatment glimepiride:
Typically, glimepiride treatment is long, under the control of glucose in the blood and urine.
Translation patients with other oral antidiabetic drugs to glimepiride:
There is no exact correlation between the dose of glimepiride and other oral sugar-reducing drugs. When replacing such other drugs glimepiride initial daily dose of the latter should be 1 mg (even if the patient is transferred to a maximum dosage of glimepiride other oral hypoglycemic drug). Any increase in the dose of glimepiride should be carried out in accordance with the recommendations given above.
It is necessary to take into account the degree and duration of effect of prior hypoglycemic agents. It may be necessary during the temporary cessation of treatment in order to avoid an additive effect, which increases the risk of hypoglycemia.
Overdose:
Symptoms: hypoglycemia (hunger, nausea, vomiting, sweating, anxiety, tachycardia, hypertension, palpitations, pain in the heart, arrhythmia, headache , dizziness, lethargy, drowsiness, restlessness, aggressiveness, impaired concentration, depression, confusion, tremor, paresis, sensory disorder, seizures of central origin). The clinical picture may resemble a stroke; may develop coma.
Treatment: If the patient is conscious – administered glucose by mouth or I / O. In severe cases, the patient should be hospitalized. When carried hypoglycemic coma infusion therapy 50% glucose solution, followed by infusion of a dilute (10%) glucose solution to maintain a blood glucose level of 100 mg% (5.5 mmol / L); possible introduction of 1 – 2 mg of glucagon or epinephrine and. Constant monitoring and maintenance of vital functions, the concentration of glucose in the blood for at least 24 – 48 hours (subject to repeated episodes of hypoglycemia). After recovery of consciousness is necessary to give the patient foods rich in easily digestible carbohydrates (to avoid a recurrence of hypoglycemia). When cerebral edema prescribed mannitol and dexamethasone.
Contraindications:
glimepiride used with caution:
Use during pregnancy and lactation:
Glimepiride is contraindicated during pregnancy. In order to avoid adverse effects on the child Glimepiride should not be administered to pregnant women; the patient should be transferred to insulin. Sick women should inform their doctor about the plans for pregnancy and go on insulin.
In experimental studies have shown that glimepiride is excreted in breast milk. Getting glimepiride with the breast milk can be harmful to the child. Therefore, glimepiride should not be given to women in lactation period. The patient should go on insulin or completely abandon breastfeeding.
Side effects:
Based on the experience with glimepiride and other sulfonylureas, you must take into account the possibility of the following side effects:
From the Metabolic: hypoglycemia (headache, “wolfish “appetite, nausea, vomiting, lethargy, sleepiness, sleep disturbances, restlessness, aggressiveness, impaired concentration, reduced alertness and reactive ability, depression, confusion, speech disorders, aphasia, disorders of vision, tremor, paresis, sensory disturbances, dizziness, loss of self-control, delirium, convulsions central origin, drowsiness and loss of consciousness up to coma, shallow respiration and bradycardia, signs of adrenergic kontrregulyatsii: sweating, anxiety, tachycardia, hypertension, palpitations, angina pectoris and cardiac arrhythmias), sodium reduction in blood (hyponatremia).
From the digestive system: sometimes nausea, vomiting, epigastric discomfort, abdominal pain, diarrhea, increase in liver transaminases. In exceptional cases, cholestasis, jaundice, hepatitis, which may lead to liver failure.
From the hematopoietic system: there may be severe disorders of the blood picture; A rare opportunity to thrombocytopenia, leykotsitopeniya, hemolytic anemia or erythropenia, granulocytopenia, agranulocytosis, and pancytopenia (due mielosupresii).
From the side of view: especially at the beginning of treatment may experience transient vision disturbances caused by changes in blood sugar levels.
Allergic reactions: sometimes there may be allergic or pseudoallergy reactions: itching, hives, rash, dyspnoea, fall in blood pressure up to anaphylactic shock. In some cases there may be allergic vasculitis or photosensitivity.
If you check at any – any side effects of those listed, any – any other undesired effects or unexpected changes, please consult your physician. Since some side effects such as severe hypoglycemia, serious changes in the blood picture, severe allergic reaction and pseudoallergy or liver failure, can under certain circumstances pose a threat to life, in the case of sudden or severe reactions. You need to immediately inform them of your doctor and in no case do not continue taking the drug without his strong recommendation.
Special warnings and precautions:
The doses of glimepiride determined by the level of glucose in blood. Glimepiride should be appointed in doses and in due time, before a heavy meal (usually before breakfast). It is very important not to skip meals after taking glimepiride. Skip reception can never be corrected by subsequently receiving higher doses. The patient should inform the doctor immediately if you receive too high a dose of glimepiride.
glimepiride treatment is carried out in conjunction with a low calorie diet low in carbohydrates. Proper diet, regular and sufficient physical exercise and, if necessary, reduction of body weight are just as important to achieve optimal control of blood sugar levels, as well as regular intake of glimepiride.
During the blood treatment glimepiride requires regular monitoring of glucose levels in the urine, and glycated hemoglobin concentrations. Performance monitor for monitoring blood glucose levels in urine and makes the detection of primary or secondary resistance to the drug. Upon reaching
compensation of diabetes increases insulin sensitivity in this regard, in the course of treatment can decrease the need for glimepiride. To avoid hypoglycaemia timely necessary to reduce the dose or cancel glimepiride. Need dosage adjustment glimepiride with the physical and emotional strain, diet change or when other factors contributing to the development of hypo – or hyperglycaemia.
The clinical symptoms of inadequate lowering of blood sugar levels (hyperglycemia) include: increased frequency of urination, excessive thirst, dry mouth and dry skin.
In the first weeks of treatment Glimepiride may increase the risk of hypoglycemia, which requires very strict monitoring of patients. Factors contributing to the development of hypoglycemia include: irregular, poor nutrition, change of dietary habits, alcohol consumption, especially in combination with skipping meals, changing the usual regime of physical activity, the simultaneous use of other drugs. Almost always, hypoglycemia can quickly be cupped instant intake of carbohydrates (glucose, or sugar, such as sugars, sweetened fruit juice or tea). Therefore, the patient must always carry at least 20 g. glucose. It may also be required to assist other patients. Artificial sweeteners are not effective in treating hypoglycemia. Severe hypoglycemia requiring immediate medical treatment under the supervision of a physician, and under certain circumstances, and hospitalization.
Precautions should be prescribed glimepiride in patients with concomitant diseases of the endocrine system affecting carbohydrate metabolism (including thyroid dysfunction, adenogipofizarnaya or adrenocortical insufficiency).
When you go to glimepiride with other drugs should take into account the degree and duration of effect of prior hypoglycemic agents. It may be necessary during the temporary cessation of treatment in order to avoid an additive effect.
In exceptional stress situations (eg trauma, surgery, infectious disease with fever) may be impaired control of blood sugar levels and may need to be in a temporary transfer of the patient to insulin.
With little effect of glimepiride or reduction steps during long-term monotherapy (secondary resistance), we recommend a combination with insulin.
It is necessary to warn patients about the increased risk of hypoglycemia when receiving NSAIDs (indomethacin. diclofenac. ibuprofen, etc..), fasting.
Alcohol can strengthen or weaken the hypoglycaemic action of glimepiride; possible development of disulfiram onopodobnogo syndrome: abdominal pain, nausea, vomiting, headache.
The clinical manifestations of hypoglycemia may be masked when taking beta – blockers (propranolol, etc.), clonidine, reserpine, guanethidine or other sympatholytic.
In the treatment of tolbutamide (1.5 g / day) for 5 – 8 years, there was an increase cardio – vascular mortality by 2.5 times.
The expiration date on the package.
Terms of pharmacy holiday – by prescription.



No Comments Yet